-40%
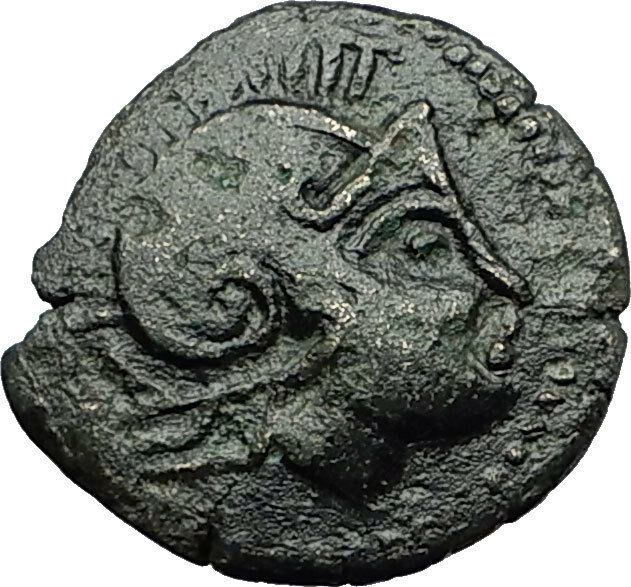
CELTIC Barbarian Europe CELTS Barbarous LYSIMACHOS as Ancient Greek Coin i59174
$ 225.72
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
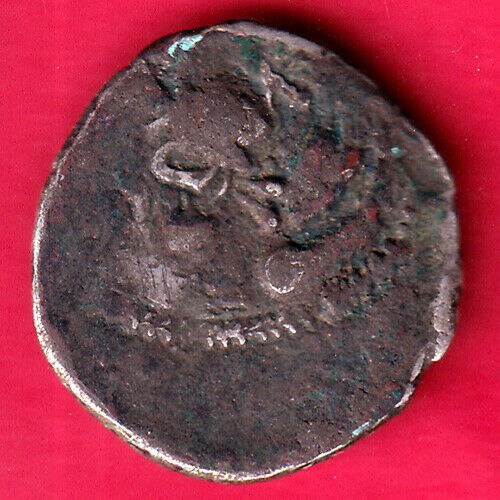
Item:i59174
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Barbarous / Celtic Tribe of Europe Issue in the style of
<="" font="">
Greek coins of Lysimachos
- King of
<="" font="">Thrace
: 323-281 B.C. -
Bronze 15mm (2.82 grams)
Barbarous (Barbarian) issue of possibly Celts of the Danube, Eastern Europe or other uncertain tribe
Reference: cf. Sear 6819; cf. Mueller 113; cf. Forrer/Weber 2731; Cf. SNG Copenhagen 1149
Barbarous, stylized head of Alexander the Great right, in crested Athenian helmet.
Blundered Greek legend above and beneath lion leaping right; spear head below.
* Numismatic Note: The Celtic / barbarian (people whom didn't speak Greek language were considered such) struck coins after the Greek coins that circulated with them for trade. Types like this allowed them to have coins to do trade with, and that is why they styled them after recognizable types of the area. The tell-tale signs of coins struck by these tribes are the stylized types which look crude in comparison to their Greek counter-parts, and the blundered legends, as the die engravers did not know the Greek language they were make these coins after.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
The
Celts
(see
Celtic
pronunciation of
) were people in
Iron Age
and
Medieval
Europe who spoke
Celtic languages
and had cultural similarities, although the relationship between ethnic, linguistic and cultural factors in the Celtic world remains uncertain and controversial. The exact geographic spread of the ancient Celts is also disputed; in particular, the ways in which the Iron Age inhabitants of Great Britain and Ireland should be regarded as Celts has become a subject of controversy.
Diachronic distribution of Celtic peoples:
Core Hallstatt territory, by the sixth century BC
Maximal Celtic expansion by 275 BC
Lusitanian area of Iberia where Celtic presence is uncertain
Areas where Celtic languages remain widely spoken today
The history of
pre-Celtic
Europe remains very uncertain. According to one theory, the common root of the Celtic languages, the
Proto-Celtic language
, arose in the Late Bronze Age
Urnfield culture
of Central Europe, which flourished from around 1200 BC. In addition, according to a theory proposed in the 19th century, the first people to adopt cultural characteristics regarded as Celtic were the people of the Iron Age
Hallstatt culture
in central Europe (c. 800–450 BC), named for the rich grave finds in
Hallstatt
, Austria. Thus this area is sometimes called the 'Celtic homeland'. By or during the later
La Tène
period (c. 450 BC up to the Roman conquest), this Celtic culture was supposed to have expanded by
trans-cultural diffusion
or
migration
to the
British Isles
(
Insular Celts
), France and the
Low Countries
(
Gauls
),
Bohemia
, Poland and much of Central Europe, the
Iberian Peninsula
(
Celtiberians
,
Celtici
,
Lusitanians
and
Gallaeci
) and
northern Italy
(
Golasecca culture
and
Cisalpine Gauls
) and, following the
Celtic settlement of Eastern Europe
beginning in
279 BC
, as far east as central
Anatolia
(
Galatians
) in modern-day
Turkey
.
The earliest undisputed direct examples of a Celtic language are the
Lepontic
inscriptions beginning in the
6th century BC
.
Continental Celtic languages
are attested almost exclusively through inscriptions and place-names.
Insular Celtic languages
are attested beginning around the
4th century
in
Ogham inscriptions
, although it was clearly being spoken much earlier. Celtic literary tradition begins with
Old Irish
texts around the
8th century
. Coherent texts of
Early Irish literature
, such as the
Táin Bó Cúailnge
("
Cattle Raid
of
Cooley
"), survive in
12th century
recensions
.
By the mid-
1st millennium
, with the expansion of the
Roman Empire
and the
Migration Period
of
Germanic peoples
, Celtic culture and
Insular Celtic languages
had become restricted to Ireland, the western and northern parts of Great Britain (
Wales
, Scotland, and
Cornwall
), the
Isle of Man
, and
Brittany
. Between the 5th and 8th centuries, the Celtic-speaking communities in these Atlantic regions emerged as a reasonably cohesive cultural entity. They had a common linguistic, religious and artistic heritage that distinguished them from the culture of the surrounding polities. By the 6th century, however, the
Continental Celtic languages
were no longer in wide use.
Insular Celtic culture diversified into that of the
Gaels
(
Irish
,
Scottish
and
Manx
) and the
Celtic Britons
(
Welsh
,
Cornish
, and
Bretons
) of the medieval and modern periods. A modern "
Celtic identity
" was constructed as part of the Romanticist
Celtic Revival
in Great Britain, Ireland, and other European territories, such as
Portugal
and
Spanish Galicia
. Today,
Irish
,
Scottish Gaelic
,
Welsh
, and
Breton
are still spoken in parts of their historical territories, and
Cornish
and
Manx
are undergoing a revival.
Area Where the Danube Area Celts would have been located
The
Danube
is a river in
Central Europe
, the
European Union
's longest and the
continent
's second longest (after the
Volga
).
Classified as an
international waterway
, it originates in the town of
Donaueschingen
--which is in the
Black Forest
of Germany--at the
confluence
of the rivers
Brigach
and
Breg
. The Danube then flows southeast for 2,872 km (1,785 mi), passing through four
Central European
capitals before emptying into the
Black Sea
via the
Danube Delta
in
Romania
and
Ukraine
.
Once a long-standing frontier of the
Roman Empire
, the river passes through or touches the borders of ten countries:
Romania
(29.0% of basin area),
Hungary
(11.6%),
Serbia
(10.2%),
Austria
(10.0%),
Germany
(7.0%),
Bulgaria
(5.9%),
Slovakia
(5.9%),
Croatia
(4.4%),
Ukraine
(3.8%), and
Moldova
(1.6%).
[1]
Its
drainage basin
extends into nine more.
Alexander III of Macedon
(20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as
Alexander the Great
, was a King (
Basileus
) of the
Ancient Greek
kingdom
of
Macedon
and a member of the
Argead dynasty
, an ancient Greek royal house. Born in
Pella
in 356 BC, Alexander succeeded his father,
Philip II
, to the throne at the age of twenty. He spent most of his ruling years on an unprecedented military campaign through Asia and northeast Africa, and by the age of thirty he had created one of the
largest empires
of the ancient world, stretching from
Greece
to
Egypt
into northwest
India
and modern-day
Pakistan
. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered one of history's most successful military commanders.
During his youth, Alexander was tutored by the philosopher
Aristotle
until the age of 16. After Philip's assassination in 336 BC, Alexander succeeded his father to the throne and inherited a strong kingdom and an experienced army. Alexander was awarded the
generalship of Greece
and used this authority to launch his father's Panhellenic project to lead the Greeks in the conquest of
Persia
. In 334 BC, he invaded the
Achaemenid Empire
, ruled
Asia Minor
, and began a
series of campaigns
that lasted ten years. Alexander broke the power of Persia in a series of decisive battles, most notably the battles of
Issus
and
Gaugamela
. He subsequently overthrew the Persian King
Darius III
and conquered the Achaemenid Empire in its entirety. At that point, his empire stretched from the
Adriatic Sea
to the
Indus River
.
Seeking to reach the "ends of the world and the Great Outer Sea", he
invaded India
in 326 BC, but was eventually forced to turn back at the demand of his troops. Alexander died in
Babylon
in 323 BC, the city he planned to establish as his capital, without executing a series of planned campaigns that would have begun with an invasion of
Arabia
. In the years following his death, a
series of civil wars
tore his empire apart, resulting in several states ruled by the
Diadochi
, Alexander's surviving generals and heirs.
Alexander's legacy includes the
cultural diffusion
his conquests engendered, such as
Greco-Buddhism
. He founded some
twenty cities that bore his name
, most notably
Alexandria
in Egypt. Alexander's settlement of Greek colonists and the resulting spread of
Greek culture
in the east resulted in a new
Hellenistic civilization
, aspects of which were still evident in the traditions of the
Byzantine Empire
in the mid-15th century and the presence of
Greek speakers in central
and
far eastern Anatolia
until the 1920s. Alexander became legendary as a classical hero in the mold of
Achilles
, and he features prominently in the history and mythic traditions of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. He became the measure against which military leaders compared themselves, and
military academies
throughout the world still teach his tactics. He is often ranked among the most influential people in human history, along with his teacher Aristotle.
<="" p="" the="" apples="" of="">
Lysimachus
(c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a
Macedonian
officer and
diadochus
(i.e. "successor") of
Alexander the Great
, who became a
basileus
("King") in 306 BC, ruling
Thrace
,
Asia Minor
and
Macedon
.
Early life and career
Lysimachus was born in 362/361 BC, to a family of
Thessalian
Greek
stock. He was the second son of
Agathocles
and his wife; there is some indication in the historical sources that this wife was perhaps named Arsinoe, and that Lysimachus' paternal grandfather may have been called Alcimachus. His father was a nobleman of high rank who was an intimate friend of
Philip II of Macedon
, who shared in Philip II’s councils and became a favorite in the
Argead court
. Lysimachus and his brothers grew up with the status of Macedonians; all these brothers enjoyed with Lysimachus prominent positions in Alexander’s circle and, like him, were educated at the Macedonian court in
Pella
.
He was probably appointed
Somatophylax
during the reign of Philip II. During Alexander's
Persian
campaigns, he was one of his immediate bodyguards. In 324 BC, in
Susa
, he was crowned in recognition for his actions in
India
. After Alexander’s death in 323 BC, he was appointed to the government of Thrace as
strategos
.
Diadochi
In 315 BC, he joined
Cassander
,
Ptolemy I Soter
and
Seleucus I Nicator
against
Antigonus I Monophthalmus
, who, however, diverted his attention by stirring up Thracian and
Scythian
tribes against him. In 309 BC, he founded
Lysimachia
in a commanding situation on the neck connecting the Chersonese with the mainland. He followed the example of Antigonus I in taking the title of king.
In 306/305 BC, he assumed the title of "King", which he held until his death at Corupedium in 282/1 BC.
In 302 BC, when the second
affiance
between Cassander, Ptolemy I and Seleucus I was made, Lysimachus, reinforced by troops from Cassander, entered Asia Minor, where he met with little resistance. On the approach of Antigonus I he retired into winter quarters near
Heraclea
, marrying its widowed queen
Amastris
, a Persian princess. Seleucus I joined him in 301 BC, and at the
battle of Ipsus
Antigonus I was defeated and slain. His dominions were divided among the victors. Lysimachus' share was
Lydia
,
Ionia
,
Phrygia
and the north coast of Asia Minor.
Kingdom of Lysimachus
Other
diadochi
Kingdom of
Cassander
Kingdom of
Seleucus I Nicator
Kingdom of
Ptolemy I Soter
Epirus
Other
Carthage
Rome
Greek colonies
Feeling that Seleucus I was becoming dangerously great, Lysimachus now allied himself with Ptolemy I, marrying his daughter
Arsinoe II
of Egypt. Amastris, who had divorced herself from him, returned to Heraclea. When Antigonus I’s son Demetrius I renewed hostilities (297 BC), during his absence in
Greece
, Lysimachus seized his towns in Asia Minor, but in 294 BC concluded a peace whereby Demetrius I was recognized as ruler of Macedonia. He tried to carry his power beyond the
Danube
, but was defeated and taken prisoner by the
Getae
king
Dromichaetes
(
Dromihete
), who, however, set him free on amicable terms. Demetrius I subsequently threatened Thrace, but had to retire due to a sudden uprising in
Boeotia
, and an attack from the King
Pyrrhus of Epirus
.
In 288 BC, Lysimachus and Pyrrhus in turn invaded Macedonia, and drove Demetrius I out of the country. Lysimachus left Pyrrhus in possession of Macedonia with the title of king for around seven months before Lysimachus invaded. For a short while the two ruled jointly but in 285 BC Lysimachus expelled Pyrrhus, seizing complete control for himself.
Later years
Domestic troubles embittered the last years of Lysimachus’ life. Amastris had been murdered by her two sons; Lysimachus treacherously put them to death. On his return, Arsinoe II asked the gift of Heraclea, and he granted her request, though he had promised to free the city. In 284 BC Arsinoe II, desirous of gaining the succession for her sons in preference to Lysimachus’ first child,
Agathocles
, intrigued against him with the help of Arsinoe II’s paternal half-brother
Ptolemy Keraunos
; they accused him of conspiring with Seleucus I to seize the throne, and Agathocles was put to death.
This atrocious deed of Lysimachus aroused great indignation. Many of the cities of Asia Minor revolted, and his most trusted friends deserted him. The widow of Agathocles and their children fled to Seleucus I, who at once invaded the territory of Lysimachus in Asia. In 281 BC, Lysimachus crossed the
Hellespont
into
Lydia
and at the decisive
Battle of Corupedium
was killed. After some days his body was found on the field, protected from birds of prey by his faithful dog. Lysimachus' body was given over to another son
Alexander
, by whom it was interred at
Lysimachia
.
Marriages and children
Lysimachus was married three times and his wives were:
First marriage:
Nicaea
a Greek Macedonian noblewoman and daughter of the powerful
Regent
Antipater
. Lysimachus and Nicaea married in c. 321 BC. Nicaea bore Lysimachus three children:
Son,
Agathocles
Daughter,
Eurydice
Daughter,
Arsinoe I
Nicaea most probably died by 302 BC.
Second marriage: Persian Princess
Amastris
. Lysimachus married her in 302 BC. Amastris and Lysimachus’ union was brief, as he ended their marriage and divorced her in 300/299 BC. Amastris had two sons from a previous marriage. During their brief marriage, Amastris may have borne Lysimachus a child, perhaps a daughter who may have been the first wife of
Ptolemy Keraunos
.
Third marriage:
Ptolemaic Greek Princess
Arsinoe II
. Arsinoe II married Lysimachus in 300/299 BC and remained with him until his death in 281 BC. Arsinoe II bore Lysimachus three sons:
Ptolemy I Epigone
Lysimachus
Philip
From an
Odrysian concubine
he had a son borne to him called
Alexander
.
See also
Belevi Mausoleum
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "Guide on How to Use My Store" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.
You may also want to do a YouTube search for the term "ancient coin collecting" for educational videos on this topic.